Vitamin D is one of the most essential nutrients for our body, yet millions of people worldwide suffer from low levels without even realizing it. Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D plays a vital role in bone health, immunity, and even mental well-being. However, due to modern lifestyles, limited outdoor exposure, and dietary gaps, Vitamin D deficiency has become a global health concern. That’s why Vitamin D supplements are more important than ever, and in 2025, the focus is on finding the best Vitamin D supplements for optimal absorption.
But before we dive into the top 8 Vitamin D supplements in 2025, it’s important to understand the causes of Vitamin D deficiency, the role of Vitamin D in our body, and how you can test your Vitamin D levels to ensure you’re getting the right amount.
Introduction to Vitamin D and Its Importance
Vitamin D isn’t just another nutrient—it’s more like a hormone that influences nearly every system in the body. Without it, calcium absorption becomes difficult, bones weaken, immunity drops, and energy levels crash. If you’ve ever wondered why you feel more tired during the winter, Vitamin D could be the missing piece.
Why Vitamin D is Called the “Sunshine Vitamin”
Vitamin D is unique because it’s one of the few nutrients that our body can produce naturally. When sunlight—specifically UVB rays—hits the skin, it triggers a chemical reaction that allows the body to produce Vitamin D3. This natural production is why Vitamin D is commonly called the sunshine vitamin. However, factors like sunscreen use, living in northern regions, and spending most of the day indoors drastically limit how much Vitamin D we produce.
Key Roles of Vitamin D in the Body
Vitamin D’s responsibilities in the body go far beyond bones. Here are some of its crucial roles:
- Bone Health: Helps regulate calcium and phosphorus absorption, preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
- Immune Function: Supports the body’s ability to fight infections and reduces inflammation.
- Muscle Strength: Plays a role in muscle contraction and balance.
- Mood Regulation: Low Vitamin D levels are linked to depression and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- Chronic Disease Prevention: Studies suggest that optimal Vitamin D levels may reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Why Vitamin D Deficiency is Becoming More Common
Despite being so essential, Vitamin D deficiency is alarmingly common. According to research, over a billion people worldwide have insufficient levels. Why? Several reasons:
- Increased urbanization leading to less sun exposure
- Heavy sunscreen use blocking Vitamin D production
- More sedentary indoor lifestyles
- Dietary habits lacking in Vitamin D-rich foods
- Age-related decline in skin’s ability to synthesize Vitamin D
This growing deficiency highlights the importance of Vitamin D supplementation, especially in 2025, when lifestyle factors are only making the issue worse.
Understanding the Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency

Before we can understand the best way to fix Vitamin D deficiency, we need to know what causes it. Deficiency doesn’t just happen overnight—it’s the result of long-term habits and health factors.
Limited Sun Exposure
The most common cause of Vitamin D deficiency is lack of sun exposure. People living in northern regions may go months without strong sunlight, especially in winter. Even in sunny areas, busy work schedules, staying indoors, or covering skin with clothing can drastically reduce Vitamin D production. Wearing sunscreen, while important for skin protection, can also block the UVB rays needed for Vitamin D synthesis.
Aging and Reduced Skin Production
As we age, our skin loses its ability to produce Vitamin D efficiently. Older adults may spend less time outdoors and also metabolize Vitamin D less effectively, making them highly vulnerable to deficiency.
Obesity and Vitamin D Storage in Fat
Vitamin D is fat-soluble, meaning it gets stored in body fat. For individuals who are overweight or obese, Vitamin D can become “trapped” in fat tissues, making it less available for the body to use. This means obese individuals often need higher Vitamin D intake to maintain healthy levels.
Medical Conditions that Affect Absorption
Certain health conditions can impair the absorption of Vitamin D from food and supplements. These include:
- Celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Liver disorders
- Kidney disease
People with these conditions are often prescribed higher doses or specialized forms of Vitamin D.
Lifestyle Factors Leading to Low Vitamin D
Modern lifestyles are also to blame. More screen time, working from home, poor diet, and even air pollution that blocks sunlight all play a role in declining Vitamin D levels. Without conscious effort, deficiency becomes almost inevitable.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Vitamin D Levels
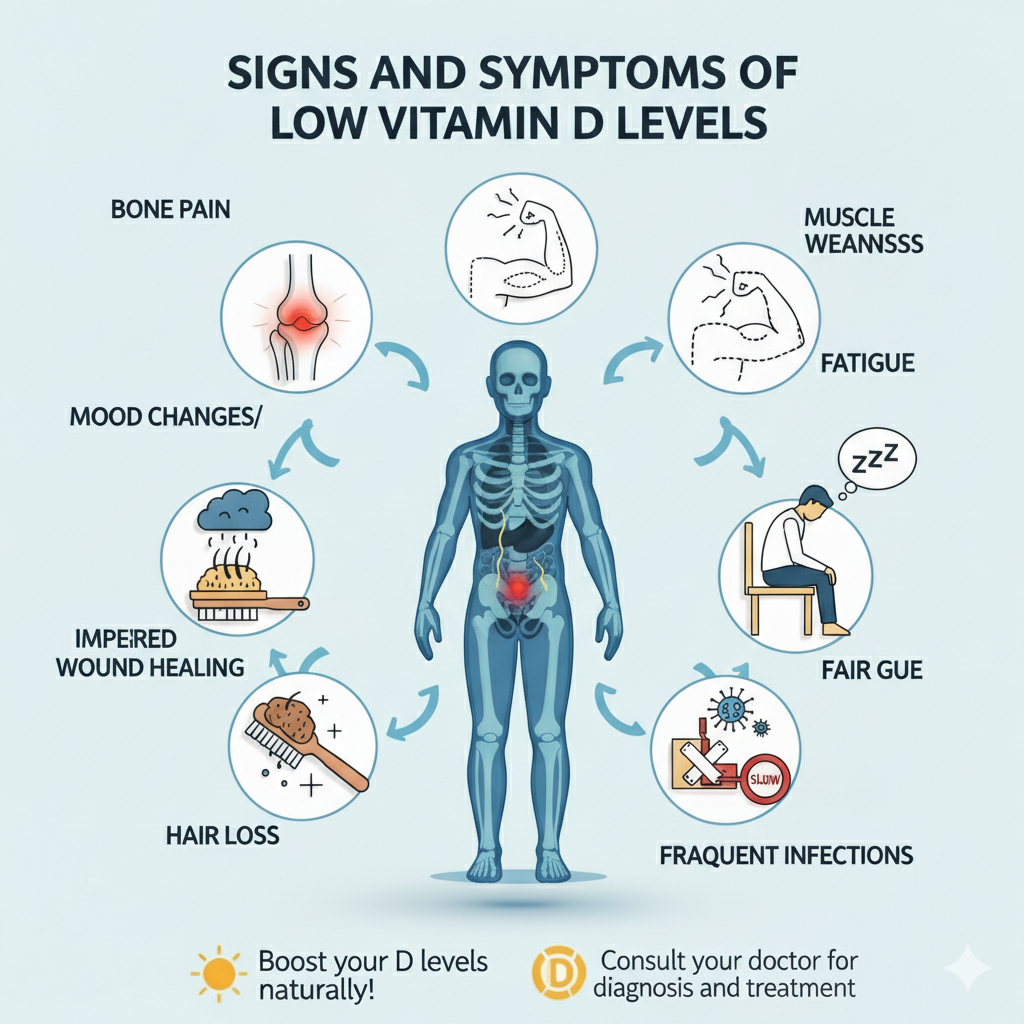
Many people don’t realize they have a Vitamin D deficiency until it leads to serious health problems. That’s why recognizing the early signs can be life-changing.
Physical Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Bone pain and muscle weakness
- Frequent illnesses or infections
- Chronic fatigue and low energy
- Slow wound healing
- Hair loss
These symptoms often creep in slowly, which is why they are commonly overlooked.
Mental Health Effects of Low Vitamin D
Low Vitamin D doesn’t just affect your body—it affects your mind. Research has found strong links between Vitamin D deficiency and mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. People with low levels often report feelings of sadness, brain fog, and lack of motivation.
Long-Term Risks of Vitamin D Deficiency
If left untreated, Vitamin D deficiency can cause serious long-term health risks:
- Osteoporosis and increased fracture risk
- Rickets in children
- Increased risk of autoimmune diseases
- Higher chance of cardiovascular issues
- Possible link to certain cancers
Clearly, maintaining healthy Vitamin D levels isn’t just about short-term health—it’s about protecting your future well-being.
How to Test for Vitamin D Levels
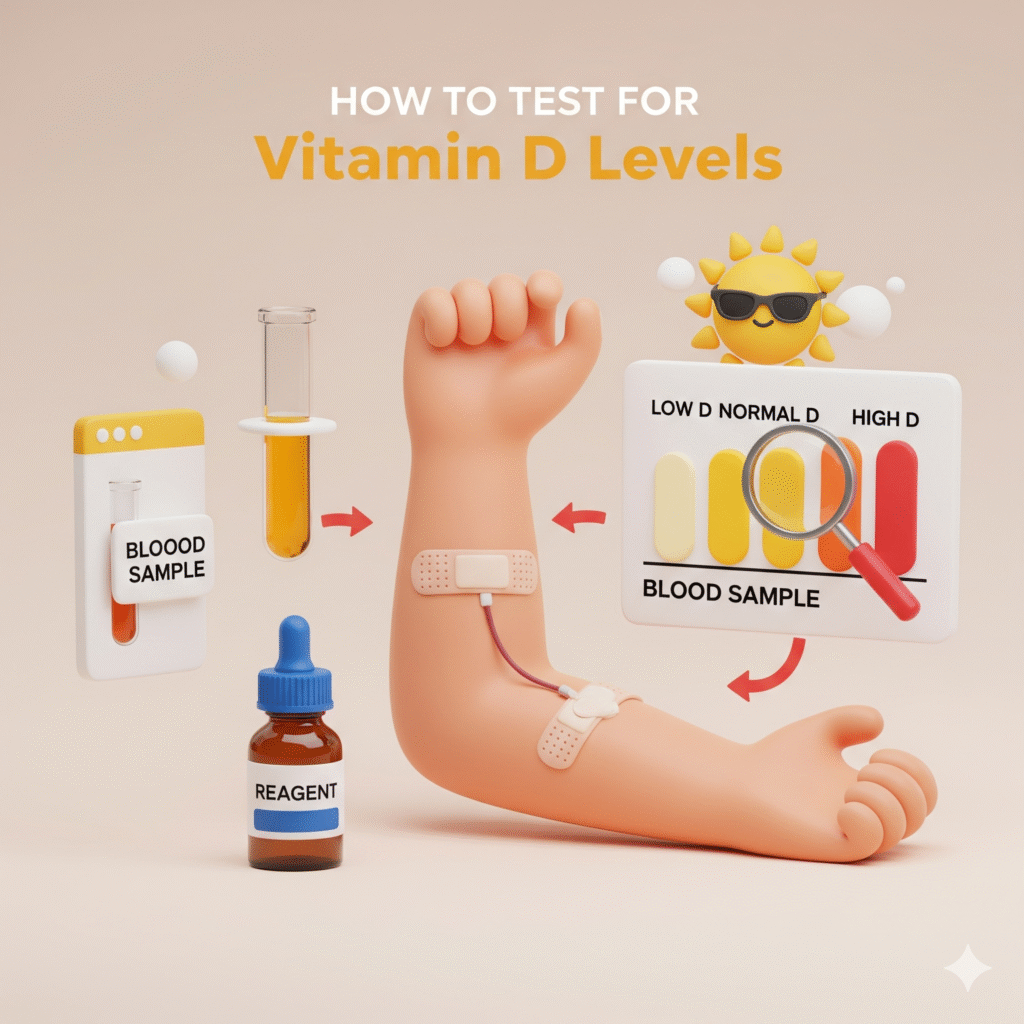
Knowing your Vitamin D status is the first step toward addressing any deficiency. Luckily, testing is simple and widely available.
What is a Vitamin D Test?
A Vitamin D test is a blood test that measures the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the main circulating form of Vitamin D in the body. This gives doctors a clear picture of whether your levels are sufficient, insufficient, or deficient.
Different Types of Vitamin D Blood Tests
- 25(OH)D Test: The most common and accurate test for overall Vitamin D levels.
- 1,25(OH)2D Test: Measures the active form of Vitamin D but is less commonly used for routine screening.
Interpreting Vitamin D Test Results
- Deficient: Less than 20 ng/mL
- Insufficient: 21–29 ng/mL
- Sufficient: 30–50 ng/mL
- Optimal Range: 50–80 ng/mL
- Toxic: Above 100 ng/mL
Understanding your results is crucial because both low and excessively high Vitamin D can cause problems.
When Should You Get Tested?
You should consider a Vitamin D test if you:
- Experience frequent fatigue, bone pain, or mood changes
- Spend little time in the sun
- Have darker skin (which reduces natural Vitamin D production)
- Are overweight or have a chronic illness
Cost and Accessibility of Vitamin D Tests
In 2025, Vitamin D tests are more accessible than ever. Many clinics, labs, and even at-home testing kits provide quick and reliable results. Costs vary depending on location, but the investment is small compared to the benefits of maintaining good health.
Choosing the Best Vitamin D Supplements in 2025
Now that we’ve covered the importance of Vitamin D, causes of deficiency, and testing, let’s move on to the next big question: How do you choose the best Vitamin D supplements in 2025?
Choosing the Best Vitamin D Supplements in 2025
With so many Vitamin D supplements on the market, it can be overwhelming to know which one is right for you. In 2025, supplement options are more advanced, offering different forms, potencies, and added nutrients to improve absorption. The key is to understand the types of Vitamin D available and how your body absorbs them best.
Vitamin D2 vs Vitamin D3 – Which is Better?
There are two main types of Vitamin D supplements: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
- Vitamin D2 comes from plant sources and is often used in fortified foods. However, studies show it is less effective at raising blood Vitamin D levels compared to D3.
- Vitamin D3 is derived from animal or plant-based sources (like lichen in vegan supplements) and is the preferred form because it is more bioavailable and stays in the bloodstream longer.
If your goal is optimal absorption and effectiveness, Vitamin D3 is the top choice in 2025, whether in capsules, drops, or gummies.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Supplement Absorption
Not all supplements are absorbed equally. Several factors influence how well your body takes in Vitamin D:
- Formulation – Liquid and softgel forms are often absorbed better than tablets.
- Dietary Fat Intake – Since Vitamin D is fat-soluble, it absorbs best when taken with a meal that includes healthy fats.
- Other Nutrients – Magnesium, Vitamin K2, and calcium work together with Vitamin D to optimize its benefits.
- Digestive Health – Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s can interfere with absorption.
Choosing a supplement designed with these factors in mind ensures you get the most benefit from each dose.
Role of Magnesium and Healthy Fats in Absorption
Magnesium is an unsung hero when it comes to Vitamin D. Without enough magnesium, your body can’t fully activate Vitamin D, making supplementation less effective. Similarly, taking Vitamin D with a meal that includes healthy fats—like avocado, nuts, or olive oil—greatly improves absorption.
That’s why some of the best Vitamin D supplements in 2025 include magnesium or recommend pairing with food for maximum benefits.
Forms of Vitamin D Supplements Available in 2025
By 2025, the supplement industry has evolved to provide Vitamin D in multiple forms to fit different preferences and needs:
- Softgels – Easy to swallow and highly absorbable.
- Capsules – Popular but may absorb slower than softgels.
- Liquid Drops – Perfect for children and people with difficulty swallowing pills.
- Gummies – Tasty option for adults and kids.
- Powders – Can be mixed into smoothies or drinks.
- Time-Release Capsules – Provide a steady release of Vitamin D throughout the day.
Having these choices makes it easier for everyone to find the right supplement for their lifestyle.
8 Best Vitamin D Supplements in 2025 for Optimal Absorption
Now that you know how to choose the right supplement, let’s explore the 8 best Vitamin D supplements in 2025. These categories represent the most effective, well-absorbed, and user-friendly forms available this year.
Supplement #1: High-Potency Vitamin D3 Softgels
Softgels are among the most effective forms of Vitamin D because they dissolve quickly and are absorbed efficiently. High-potency softgels are great for people with severe deficiencies who need to raise their levels fast. Many options in 2025 come with added oils (like olive or coconut oil) to boost absorption naturally.
These supplements are ideal for adults who want strong bone health, improved immunity, and a convenient once-a-day dose.
Supplement #2: Plant-Based Vitamin D Supplements
With more people adopting vegetarian and vegan lifestyles, plant-based Vitamin D has grown in popularity. In 2025, lichen-derived Vitamin D3 has become the gold standard for vegan-friendly options. Unlike older plant-based D2 supplements, these vegan D3 supplements provide the same absorption and effectiveness as animal-derived sources.
Perfect for those who follow a plant-based diet or prefer cruelty-free supplements without sacrificing effectiveness.
Supplement #3: Liquid Vitamin D Drops
Liquid Vitamin D is one of the most versatile forms. Just a few drops under the tongue or in a drink can provide your daily dose. Because it bypasses part of the digestive process, it’s absorbed quickly and effectively.
This form is especially useful for children, elderly individuals, or anyone who struggles with swallowing pills. In 2025, many liquid Vitamin D drops come in measured droppers, making it easy to customize dosage.
Supplement #4: Vitamin D with Magnesium and K2
Taking Vitamin D alone is good, but pairing it with magnesium and Vitamin K2 makes it great. Magnesium helps activate Vitamin D in the body, while K2 ensures calcium goes to the bones instead of the arteries. This powerful combination supports not just bone health but also heart health.
Supplements that combine these nutrients are some of the most recommended in 2025 for optimal absorption and safety.
Supplement #5: Vegan-Friendly Vitamin D Options
Beyond lichen-based D3, other innovative vegan-friendly forms are available in 2025. These supplements use advanced plant extractions, ensuring they are free from animal products and allergens. Many also come fortified with supportive nutrients like zinc or omega-3s from algae, enhancing their effectiveness.
These options are perfect for those who prioritize both health and ethical choices.
Supplement #6: Time-Release Vitamin D Capsules
For people who struggle with fluctuating Vitamin D levels, time-release capsules are an excellent innovation. Instead of releasing all at once, they provide a steady flow of Vitamin D throughout the day, mimicking the body’s natural rhythm.
This makes them particularly effective for individuals with absorption issues or those who need a more consistent supply.
Supplement #7: Vitamin D Gummies for Adults and Kids
Who says supplements have to taste bad? Gummies are one of the most popular Vitamin D forms in 2025 because they are fun, tasty, and easy to take. Available in various flavors, they make supplementation simple for kids and even adults who dislike swallowing pills.
The best options come with natural sweeteners and no artificial colors, ensuring they’re both effective and healthy.
Supplement #8: Multivitamin with High Vitamin D Content
For people who prefer an all-in-one solution, multivitamins with added Vitamin D are a great choice. Many of these multivitamins in 2025 now contain higher doses of D3, ensuring users meet their daily needs while also getting other essential nutrients like B vitamins, zinc, and iron.
This is especially useful for busy individuals who don’t want to take multiple pills each day.
How to Maximize the Absorption of Vitamin D Supplements
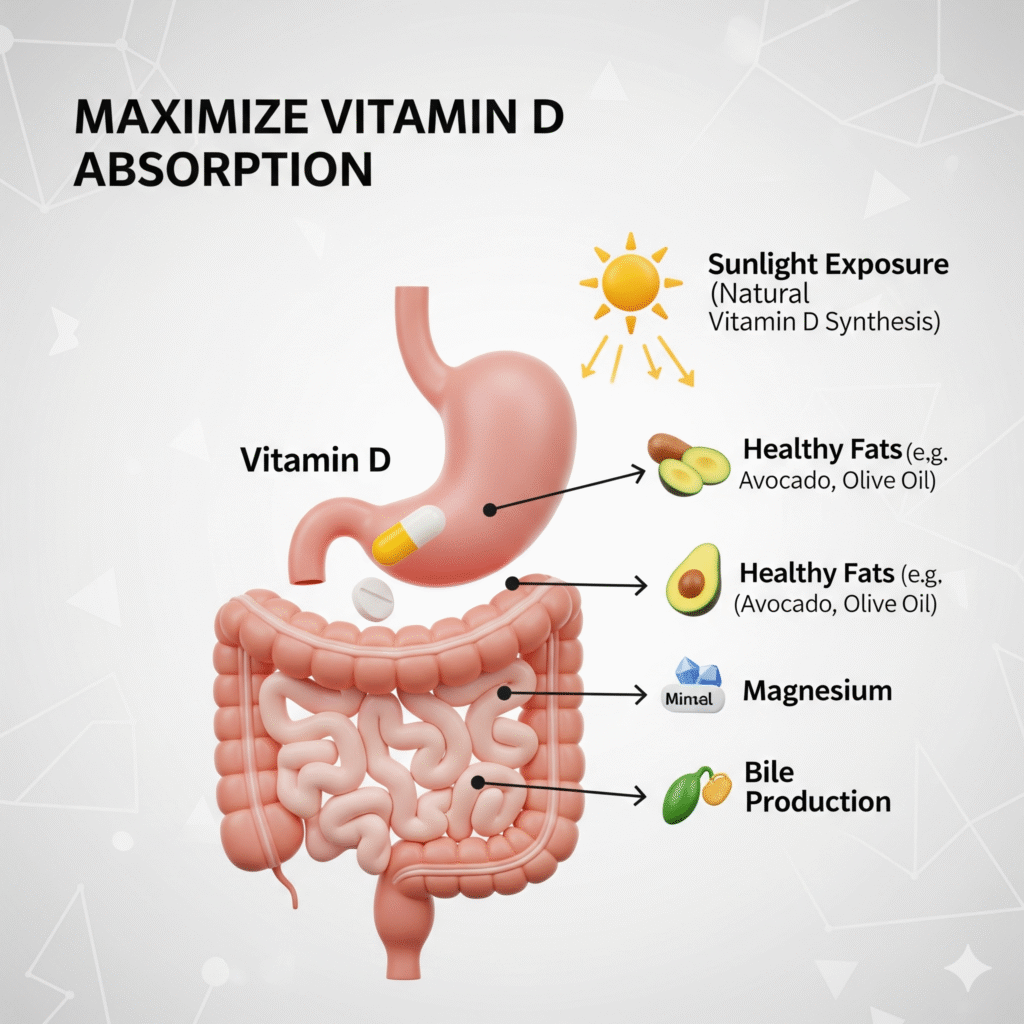
Even the best supplement won’t help if your body can’t absorb it properly. Here are the key strategies in 2025 to get the most from your Vitamin D supplement.
Best Time of Day to Take Vitamin D
Research shows that Vitamin D is best absorbed when taken with meals that include healthy fats. Many experts recommend taking it in the morning or at lunchtime because taking Vitamin D too late may interfere with melatonin production and sleep.
Should You Take Vitamin D with Food?
Yes, absolutely. Since Vitamin D is fat-soluble, taking it with a meal rich in good fats—like salmon, avocado, or nuts—boosts absorption significantly. Taking it on an empty stomach reduces its effectiveness.
Combining Vitamin D with Other Nutrients
To enhance absorption and effectiveness:
- Pair with Magnesium to activate Vitamin D.
- Add Vitamin K2 to ensure calcium is deposited in bones.
- Maintain adequate calcium intake to maximize bone benefits.
Avoiding Common Mistakes When Supplementing Vitamin D
- Don’t take Vitamin D inconsistently—daily or weekly dosing works best.
- Avoid overdosing, as high levels can lead to toxicity.
- Don’t rely on supplements alone—get sun exposure and eat Vitamin D-rich foods when possible.
Recommended Dosage of Vitamin D in 2025

Dosage is crucial. Too little Vitamin D won’t fix a deficiency, and too much can cause harm. In 2025, health organizations have refined dosage recommendations to match new research.
General Daily Recommendations
- Adults: 600–800 IU per day for maintenance
- Seniors (65+): 800–2000 IU per day to support bone strength
- Children: 400–600 IU per day
Dosage for Children, Adults, and Seniors
- Infants (0–12 months): 400 IU daily
- Children (1–18 years): 600–1000 IU daily
- Adults (19–64 years): 800–2000 IU daily depending on lifestyle
- Seniors (65+): 1000–2000 IU daily to reduce fracture risk
Safe Upper Limits for Vitamin D Supplementation
The safe upper limit is around 4000 IU per day for most adults, but higher doses may be prescribed under medical supervision for deficiency treatment.
Risks of Vitamin D Overdose
Too much Vitamin D can lead to hypercalcemia, a condition where calcium builds up in the blood. Symptoms include nausea, kidney problems, and confusion. Always follow dosage guidelines and test levels if taking high doses.
Natural Ways to Boost Vitamin D Levels Without Supplements
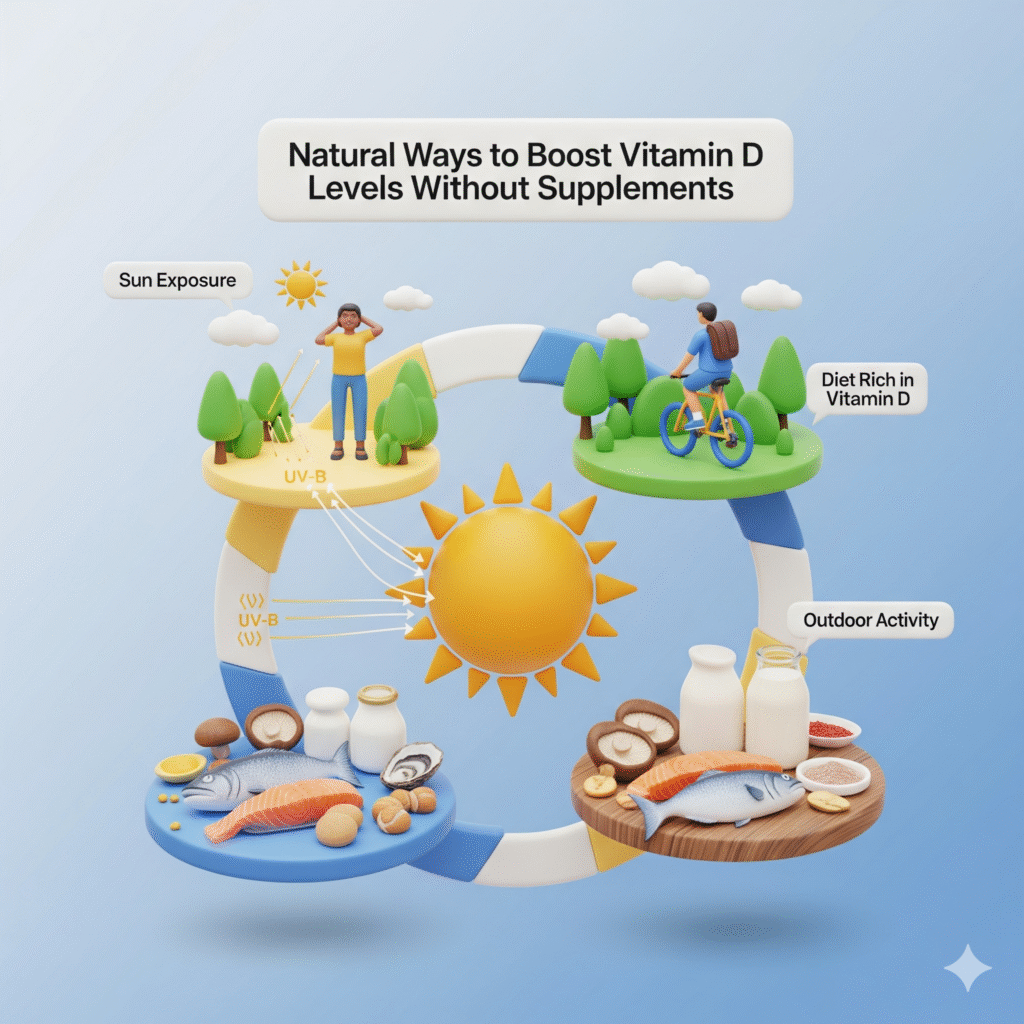
Supplements are an excellent way to maintain Vitamin D levels, but they aren’t the only method. By 2025, more people are exploring natural strategies to balance their Vitamin D without always relying on pills or drops. Lifestyle and diet changes can play a huge role in naturally improving Vitamin D levels.
Sunlight Exposure and Safe Tanning
The most natural and effective way to increase Vitamin D is through sunlight. Spending 10–30 minutes outdoors a few times a week can be enough for many people, depending on their skin tone and location.
- Lighter skin tones typically need less sun exposure to produce Vitamin D.
- Darker skin tones require more sunlight due to higher melanin levels.
However, balance is important. Overexposure can lead to sunburn and increase skin cancer risk. That’s why experts recommend short, safe periods of sun exposure without sunscreen, followed by sun protection if staying outdoors longer.
Vitamin D-Rich Foods
While only a few foods naturally contain Vitamin D, adding these options to your diet can make a big difference:
- Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel
- Egg yolks
- Mushrooms exposed to sunlight
- Fortified foods such as cereals, plant-based milks, and juices
Though food alone often isn’t enough to maintain optimal levels, it complements supplements and sunlight effectively.
Lifestyle Habits That Improve Vitamin D
- Outdoor activities like walking, gardening, or cycling help boost Vitamin D naturally.
- Healthy weight management improves Vitamin D circulation in the body.
- Balanced diet with healthy fats supports absorption.
In 2025, wellness experts emphasize combining outdoor exposure, diet, and supplements (if necessary) for a well-rounded Vitamin D strategy.
Who Should Take Vitamin D Supplements?
Not everyone needs the same amount of Vitamin D. Some people can maintain healthy levels through lifestyle alone, while others need supplements to avoid deficiency. In 2025, health professionals highlight several high-risk groups that benefit most from supplementation.
High-Risk Groups for Vitamin D Deficiency
- People who spend little time outdoors
- Those with darker skin pigmentation
- Individuals who are overweight or obese
- People living in regions with long winters and minimal sunlight
For these groups, supplementation is often essential to prevent deficiency.
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Vitamin D plays a vital role in pregnancy, supporting both the mother’s bone health and the baby’s skeletal development. Deficiency during pregnancy can lead to complications such as preeclampsia or low birth weight. Breastfeeding women also need adequate Vitamin D to ensure proper levels for their infants.
Doctors in 2025 often recommend 1000–2000 IU daily for pregnant and nursing mothers, depending on blood test results.
People Living in Low-Sunlight Areas
Those living far from the equator often experience long winters with limited sunlight. Even during summer, cloudy or polluted areas may block UVB rays, making supplementation a must.
Elderly and Chronically Ill Individuals
Older adults are more likely to suffer from Vitamin D deficiency because their skin produces less with age. People with chronic illnesses—like kidney disease, liver disorders, or digestive conditions—also have difficulty absorbing Vitamin D. For these groups, supplements are not just beneficial but often medically necessary.
Vitamin D and Bone Health
One of the most well-known benefits of Vitamin D is its essential role in bone health. Without enough Vitamin D, calcium absorption plummets, and bones become fragile.
Role in Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D acts like a gatekeeper, ensuring calcium from food or supplements is absorbed into the bloodstream. Without Vitamin D, even a calcium-rich diet won’t strengthen bones properly.
Preventing Osteoporosis and Fractures
In 2025, osteoporosis remains one of the most common bone diseases, especially in women after menopause. Adequate Vitamin D levels help reduce the risk of fractures by strengthening both bone density and muscle function, improving balance and reducing falls.
Vitamin D’s Role in Childhood Bone Development
For children, Vitamin D is equally crucial. Deficiency can cause rickets, a condition that leads to soft, weak bones. Ensuring children get enough Vitamin D through sunlight, diet, or supplements supports healthy growth and strong skeletal development.
Bone health is one of the strongest arguments for keeping Vitamin D levels in the optimal range throughout life.
Vitamin D and Immune System Support
By 2025, one of the most researched aspects of Vitamin D is its connection to immunity. The pandemic years made people more aware of the role nutrients play in fighting illness, and Vitamin D has proven to be one of the most important.
Fighting Infections Naturally
Vitamin D boosts the production of antimicrobial peptides, natural compounds that help the body fight bacteria and viruses. People with healthy Vitamin D levels often experience fewer colds, flu episodes, and respiratory infections.
Vitamin D and Autoimmune Diseases
Research continues to show that Vitamin D may help regulate the immune system, preventing it from attacking healthy cells. Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes.
Vitamin D’s Role in Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases, from arthritis to heart conditions. Vitamin D helps modulate inflammatory responses, making it a valuable nutrient for overall long-term health.
For anyone looking to strengthen immunity in 2025, Vitamin D remains a must-have nutrient.
Vitamin D and Mental Health
Beyond physical health, Vitamin D has a major impact on mental well-being. In 2025, studies highlight the growing recognition of Vitamin D’s role in mood regulation and cognitive function.
Connection Between Vitamin D and Depression
Low Vitamin D levels are strongly associated with depression. People with deficiency often report fatigue, sadness, and lack of motivation. Supplementing with Vitamin D has been shown to improve mood, particularly in those with low baseline levels.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) and Vitamin D
SAD is a type of depression that occurs during winter months when sunlight is scarce. Since sunlight directly affects Vitamin D production, many experts recommend supplementation as part of managing SAD symptoms.
Cognitive Health and Brain Function
Vitamin D receptors are found in areas of the brain related to memory and learning. Research suggests that maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels may reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia as people age.
In short, Vitamin D is not just for bones and immunity—it’s also a powerful ally for brain health and emotional balance.
Future of Vitamin D Supplements Beyond 2025
The future of Vitamin D supplementation looks promising, with science and technology shaping more personalized and effective options.
Technological Advancements in Supplement Formulation
By 2025, advanced delivery systems like nano-encapsulation are improving Vitamin D absorption and stability. These innovations ensure higher bioavailability with smaller doses.
Personalized Nutrition and Vitamin D
Genetic testing and personalized nutrition are becoming mainstream. Soon, people will be able to tailor their Vitamin D dosage based on genetic markers, lifestyle, and health conditions, ensuring truly individualized care.
Global Awareness and Preventive Healthcare Trends
Governments and health organizations worldwide are promoting Vitamin D awareness. With more research confirming its role in immunity, mental health, and chronic disease prevention, Vitamin D supplementation is moving from being an option to being a preventive healthcare necessity.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is far more than just a bone-health nutrient—it’s a cornerstone of overall well-being. From boosting immunity and protecting mental health to ensuring strong bones and preventing chronic illness, its benefits touch nearly every aspect of life.
In 2025, the best way to maintain healthy Vitamin D levels is a balanced approach:
- Regular sun exposure (when safe)
- Vitamin D-rich foods
- Smart supplementation tailored to individual needs
Whether you prefer softgels, drops, or gummies, the right supplement can make a huge difference. And with new advancements in absorption and personalization, Vitamin D supplementation is becoming more effective than ever.
Don’t wait until symptoms appear—test your Vitamin D levels regularly, supplement wisely, and invest in your long-term health.
FAQs
Can you take Vitamin D every day safely?
Yes, Vitamin D is safe to take daily in recommended amounts. Most adults benefit from 800–2000 IU per day, but it’s important not to exceed the upper safe limit of 4000 IU unless directed by a doctor.
How long does it take to fix Vitamin D deficiency?
It typically takes 8–12 weeks of consistent supplementation to raise Vitamin D levels to the optimal range, depending on the severity of deficiency and the dosage taken.
Can Vitamin D deficiency cause fatigue?
Yes, one of the most common symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency is chronic fatigue. Restoring levels often improves energy and reduces tiredness.
Is sunlight enough to maintain Vitamin D levels?
For some people, yes. However, factors like skin tone, climate, and lifestyle often make sunlight alone insufficient. That’s why supplements are often recommended.
What is the best way to test Vitamin D levels at home?
At-home Vitamin D test kits are widely available in 2025. They require a small blood sample (finger prick) and provide results within days, helping you track your levels conveniently.


Leave a Reply