Understanding Early Pregnancy Detection
Every woman who’s been trying to conceive knows that the wait between ovulation and a missed period can feel endless. The anticipation, the overanalyzing of every twinge or symptom—it’s all part of the emotional rollercoaster. But what if your body is already whispering clues before your period is officially late? Recognizing early pregnancy signs before a missed period can give you an idea of what’s happening internally, even before you see those two pink lines.

Pregnancy starts long before most people realize it. The earliest indicators often show up as subtle physical or emotional changes—shifts you might overlook if you’re not paying attention. In this article, we’ll explore how to identify those early pregnancy signs, understand your body’s signals, and learn the best time and method for taking a pregnancy test for accurate results.
What Happens in the Body Right After Conception
Pregnancy begins the moment a sperm successfully fertilizes an egg. This usually happens in the fallopian tube, and within a few days, the fertilized egg (now called a zygote) travels to the uterus for implantation. Around six to ten days after ovulation, the egg attaches to the uterine wall—this is implantation. Once implanted, your body starts producing the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the same hormone that pregnancy tests detect.
Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone also start increasing rapidly, preparing your body to nourish and protect the growing embryo. These hormonal surges cause most early pregnancy symptoms—fatigue, breast tenderness, and even mood swings. It’s incredible how quickly your body begins to adjust, even before your missed period signals what’s happening.
Why Identifying Pregnancy Before a Missed Period Matters
Catching early pregnancy signs before your missed period isn’t just about curiosity—it’s about care. Early recognition helps you start making healthy choices sooner. Avoiding alcohol, managing stress, and eating nutrient-rich foods can positively impact early fetal development.
For those trying to conceive, early detection provides emotional reassurance and allows you to prepare mentally and physically for the journey ahead. For others who weren’t planning a pregnancy, recognizing signs early gives you more time to make informed decisions about your health.
But it’s also important to remember: early signs vary widely. Some women experience them just days after conception, while others feel nothing until weeks later. Knowing what to look for can make a big difference in interpreting your body’s cues correctly.
Common Early Signs of Pregnancy Before a Missed Period





Recognizing pregnancy before your missed period involves tuning into subtle physical changes. Here are the most common signs:
Fatigue and tiredness: Feeling unusually exhausted even after a good night’s sleep? That’s one of the earliest pregnancy indicators. Your body is producing more progesterone, which slows things down, making you feel drowsy and drained.
Nausea and food aversions: Morning sickness doesn’t always wait until after your missed period. Some women feel queasy or develop sudden aversions to strong smells and certain foods within a week of conception.
Tender or swollen breasts: Your breasts might feel sore, fuller, or more sensitive. This happens due to rising hormone levels, preparing your body for potential breastfeeding.
Frequent urination: You might find yourself visiting the bathroom more often than usual. Increased blood flow to the kidneys and hormonal changes trigger this early pregnancy symptom.
Light spotting and implantation bleeding: Around the time your period is due, you might notice light pink or brown spotting. Unlike a regular period, implantation bleeding is short and very light.
Mild cramping and bloating: These sensations often mimic PMS cramps but can be due to the uterus expanding slightly after implantation.
Mood swings: Emotional ups and downs can occur early due to hormonal surges, even before your missed period.
Uncommon Yet Early Pregnancy Symptoms to Watch For

While most people are familiar with classic early pregnancy signs like nausea or fatigue, there are a few lesser-known symptoms that might appear even before your missed period. These are the subtle hints that can easily be dismissed as normal body fluctuations—but together, they could indicate early pregnancy.
Metallic taste in mouth: Some women report a strange metallic or “penny-like” taste soon after conception. This happens due to increased estrogen levels, which can alter your taste perception. You may find certain foods that once tasted fine suddenly taste off or even repulsive.
Increased sense of smell: Your nose may turn into a super-sniffer! Elevated estrogen and hCG can heighten your sensitivity to scents, making you notice fragrances (good or bad) that didn’t bother you before.
Headaches or dizziness: The combination of hormonal changes, lower blood sugar levels, and increased blood volume can lead to mild headaches or spells of dizziness. If you’re experiencing this before your period, it could be your body adjusting to pregnancy.
Slight body temperature changes: Tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) can offer early insights. After ovulation, your BBT rises slightly and remains high if conception occurs. A sustained rise in temperature for more than two weeks may be one of the earliest pregnancy indicators.
These uncommon signs may seem small, but when several occur together—especially alongside fatigue, breast tenderness, or nausea—they could point toward pregnancy before your period is even late.
Understanding Implantation Bleeding vs. Period
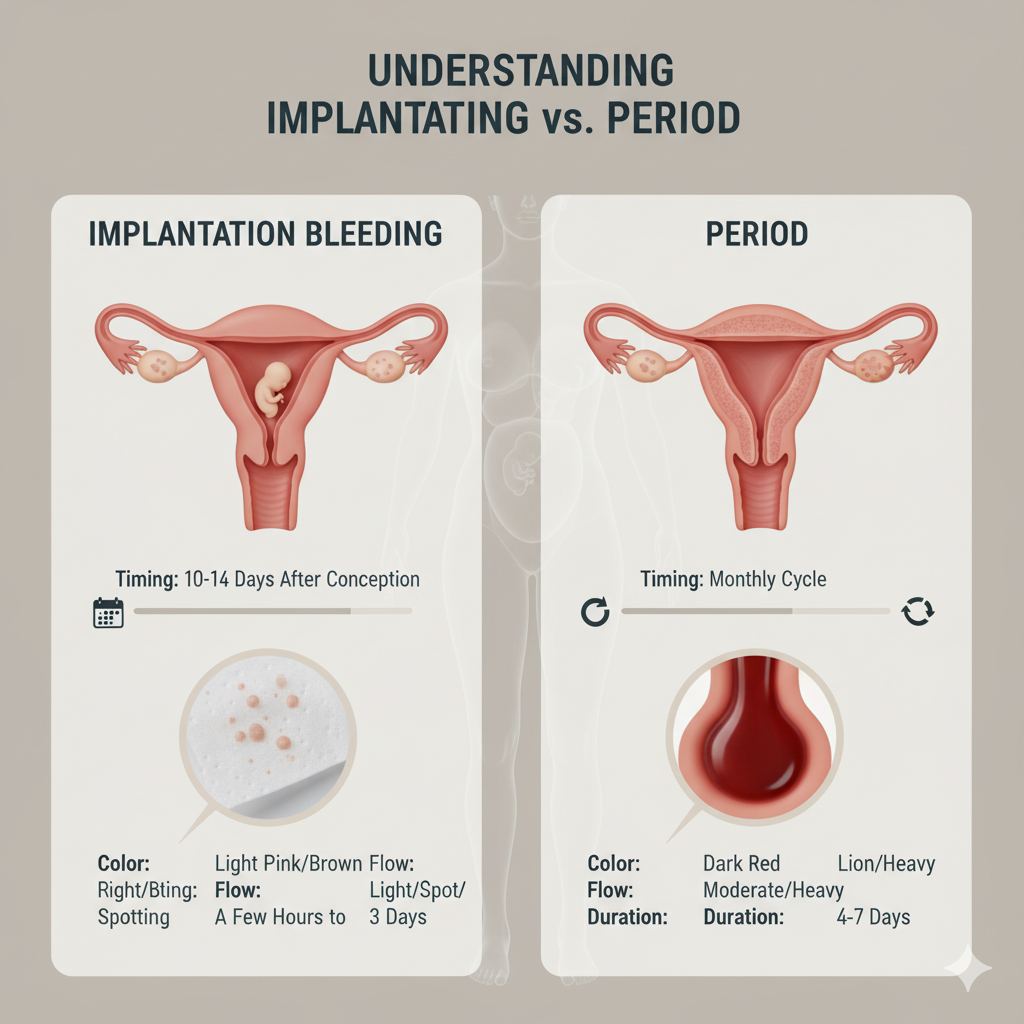
One of the trickiest parts of early pregnancy is distinguishing implantation bleeding from your regular period. Implantation bleeding occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining—typically 6 to 12 days after ovulation.
Here’s how to tell the difference:
| Feature | Implantation Bleeding | Period |
| Color | Light pink or brown | Bright or dark red |
| Flow | Very light spotting | Moderate to heavy flow |
| Duration | 1–3 days | 4–7 days |
| Timing | About a week before your period | On your expected date |
Implantation bleeding doesn’t contain clots and is often accompanied by mild cramping or a pulling sensation. If you notice such spotting earlier than your expected period date, it may be a sign that implantation has occurred and pregnancy hormones are just beginning to rise.
To track this, note the color, amount, and timing of the bleeding in your fertility journal or app. It’s an important clue when identifying early pregnancy before a missed period.
Hormonal Changes Responsible for Early Pregnancy Signs
Hormones drive everything in early pregnancy. The main player is hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which starts increasing shortly after implantation. hCG signals your body to maintain the uterine lining and stop your period.
Next comes progesterone, which helps sustain pregnancy by thickening the uterine lining and relaxing your muscles. It’s the reason you feel bloated, tired, or constipated during early pregnancy.
Then there’s estrogen, responsible for breast tenderness and mood swings. Estrogen and progesterone work together to prepare your body for nurturing the embryo.
Within days of implantation, these hormonal changes can produce noticeable symptoms—even before a missed period. Understanding their role helps you interpret why your body feels different and when it might be time to take a test.
When Can Pregnancy Tests Detect hCG Before a Missed Period

Pregnancy tests detect hCG levels in your urine or blood. After implantation, hCG doubles approximately every 48–72 hours. While most tests are designed to detect hCG around the time of your missed period, some highly sensitive tests can pick it up earlier—sometimes 6–8 days after ovulation.
However, not every woman’s hCG levels rise at the same rate. If you test too soon, your body may not have produced enough hCG to show a positive result. The most accurate time to test is about one week after your missed period, but if you’re testing early, choose a high-sensitivity home pregnancy test that can detect lower levels of hCG (around 10 mIU/mL).
To increase your chances of an accurate reading, test first thing in the morning when your urine is most concentrated.
How to Take a Pregnancy Test Correctly
If you’re testing before your missed period, accuracy depends on timing and method. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide to ensure you get the best results:
- Choose a sensitive early detection test. Look for one that can detect low hCG levels.
- Use first-morning urine. It’s the most concentrated, increasing the chance of detection.
- Follow instructions carefully. Different brands have slightly different testing methods—some require dipping, others midstream use.
- Wait the correct amount of time. Don’t read the result too early or too late.
- Check results under natural light. Dim lighting may make faint lines hard to interpret.
If you’re testing very early (before your period), remember that even a negative result doesn’t mean you’re not pregnant—it might just be too soon. Waiting another 48 hours and retesting can make a big difference.
Understanding Faint Lines and Indeterminate Results
Seeing a faint line on a pregnancy test can spark both excitement and confusion. Does it mean you’re pregnant or not? The truth is, any visible second line—no matter how faint—often indicates the presence of hCG in your system, suggesting early pregnancy.
However, a faint line can also appear due to:
- Testing too early
- Diluted urine (from drinking too much water)
- Evaporation lines (if read after the recommended time)
If your line is faint but visible within the time limit, wait two days and retest. hCG doubles every 48–72 hours, so a stronger line on the next test is a good confirmation.
False Positives and Negatives: What You Need to Know
False results happen more often than people think.
False positives (a positive result when you’re not pregnant) are rare but possible due to:
- Certain fertility medications containing hCG
- Chemical pregnancies (very early miscarriages)
- Testing errors
False negatives (a negative result when you’re actually pregnant) are much more common, especially when testing too early or using diluted urine.
To minimize errors:
- Test after your first missed period day for higher accuracy
- Follow all instructions precisely
- Avoid testing late at night after drinking lots of fluids
Understanding these nuances prevents unnecessary confusion and helps you interpret results correctly.
Tracking Basal Body Temperature for Early Pregnancy Signs
If you’ve been charting your basal body temperature (BBT), you already have a head start in detecting early pregnancy before a missed period. BBT is your body’s lowest resting temperature, typically measured right after waking up. During ovulation, progesterone causes your BBT to rise slightly—usually by 0.4°F to 1.0°F—and it remains elevated until your next period.
However, if you become pregnant, your BBT will stay high for more than 16 consecutive days after ovulation. This sustained rise is a strong early indicator of pregnancy.
Here’s how to track it effectively:
- Use a digital basal thermometer for accurate readings.
- Take your temperature every morning at the same time before getting out of bed.
- Record your readings on a chart or fertility app.
- Watch for a pattern: a dip before ovulation, then a rise afterward.
- If your temperature stays high well past your typical luteal phase, pregnancy is a strong possibility.
BBT charting is an excellent natural method for those who prefer to observe body changes before taking a test. It’s not foolproof, but when paired with other early symptoms—like tender breasts or nausea—it can provide strong hints that conception has occurred.
Cervical Mucus Changes as Early Indicators of Pregnancy
Your cervical mucus changes throughout your menstrual cycle, influenced by fluctuating hormones. Observing its consistency and appearance can also reveal early pregnancy clues before your missed period.
After ovulation, cervical mucus typically becomes dry or sticky. But if conception occurs, progesterone and estrogen levels cause your mucus to remain thick, creamy, or milky white. You may even notice increased discharge, which helps protect the cervix from infection during early pregnancy.
Here’s what to look for:
- Color: White or pale yellow (not green or gray)
- Texture: Creamy or lotion-like
- Amount: Slightly more than usual post-ovulation
While cervical mucus alone can’t confirm pregnancy, when combined with other signs—like fatigue, breast tenderness, and implantation spotting—it becomes a valuable part of the early detection puzzle.
Lifestyle Factors That Can Mimic Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Sometimes, your body can trick you into believing you’re pregnant when you’re not. Several lifestyle factors and hormonal fluctuations can mimic early pregnancy signs. Understanding these helps you avoid false assumptions and unnecessary stress.
Stress: Emotional stress affects hormone levels, particularly cortisol, which can delay ovulation or menstruation—leading to bloating, fatigue, and mood swings that resemble pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalance: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid issues can create symptoms such as breast tenderness, nausea, or irregular periods.
Diet and caffeine: Sudden dietary changes, caffeine withdrawal, or dehydration can also cause headaches, fatigue, or dizziness similar to early pregnancy.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): PMS symptoms can overlap heavily with early pregnancy—breast soreness, irritability, bloating, and mild cramping. The key difference is that pregnancy symptoms tend to last longer and may intensify instead of fading once your period arrives.
Keeping track of your cycle, lifestyle habits, and emotional state can help you distinguish true pregnancy signs from those caused by external factors.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Even if you’re testing early, professional confirmation is always important. You should consult a healthcare provider if:
- You’ve had a positive home test
- You’ve missed your period for more than a week
- You’re experiencing severe cramps, dizziness, or heavy bleeding
Early prenatal care ensures both your health and your baby’s well-being. Healthcare professionals can confirm pregnancy through more sensitive tests and recommend essential vitamins, like folic acid, to support fetal development.
If your test results are unclear or symptoms persist despite negative tests, it’s also wise to visit a professional. Hormonal imbalances, cysts, or thyroid conditions can sometimes mimic pregnancy symptoms and need medical evaluation.
Emotional Aspects of Waiting for Pregnancy Confirmation
The emotional rollercoaster of the two-week wait—the time between ovulation and your expected period—can be one of the most challenging phases of trying to conceive. Every twinge, craving, or wave of fatigue might feel like a clue, but uncertainty can be emotionally draining.
Here’s how to stay grounded during this time:
- Focus on self-care. Prioritize rest, hydration, and gentle activities that bring peace.
- Avoid overtesting. Testing too early can cause disappointment due to false negatives.
- Stay hopeful but realistic. Remember, every body is different—some pregnancies take longer to reveal themselves.
- Connect with others. Talking with supportive friends or online communities can make the wait less isolating.
Whether you’re hoping for a positive test or just seeking clarity, maintaining emotional balance helps you approach the process with a calm and confident mindset.
Trusting Your Body and Knowing When to Test
Identifying pregnancy before a missed period is part science, part intuition. Your body often gives early hints—some subtle, some obvious—if you know where to look. From implantation bleeding to temperature shifts and hormonal symptoms, the early stages of pregnancy are full of quiet signals.
However, remember that while these signs can be encouraging, the only true confirmation comes from a pregnancy test and, ultimately, a healthcare professional. If you suspect you’re pregnant, test at the right time and follow up for confirmation.
Above all, listen to your body. It has a way of communicating what’s happening within—even before modern tests can detect it. Whether this cycle leads to a positive result or not, understanding your body’s rhythm is always a step toward better reproductive health.
FAQs
- Can I be pregnant even if I test negative before my period?
Yes, it’s possible. If you test too early, your hCG levels might still be too low to detect. Wait two to three days and test again for more accurate results. - How early can hCG be detected in urine?
Some sensitive pregnancy tests can detect hCG as early as 6–8 days after ovulation, though it’s more reliable to test after your period is due. - Is implantation bleeding always a sign of pregnancy?
Not always, but it’s a common early indicator. Implantation bleeding is light, short, and usually occurs a few days before your expected period. - Should I use a digital or line pregnancy test?
Both work well, but digital tests can be easier to interpret, showing a clear “pregnant” or “not pregnant” message. - Can stress delay my period and mimic pregnancy symptoms?
Absolutely. Stress can alter your hormonal balance, causing delayed ovulation or PMS symptoms that feel like early pregnancy signs.


Leave a Reply