Viral fever is something almost everyone experiences at some point in life. While it can make you feel weak, tired, and uncomfortable, the good news is that recovery is usually possible with the right care, rest, and treatment. Knowing how to recover from viral fever fast is important not only for your health but also to return to your daily routine quickly. In this article, we will dive deep into the causes, symptoms, mandatory tests, home remedies, and proven tips to get back on your feet as soon as possible.
Understanding Viral Fever
What is Viral Fever?
Viral fever is a condition caused by an infection due to viruses entering the body. Unlike bacterial infections, which can often be treated with antibiotics, viral infections usually need supportive care until the body’s immune system clears the infection. The term “viral fever” is often used when a person experiences a rise in body temperature due to a viral infection.
The fever itself is not a disease but rather a symptom that the body is fighting off an infection. The body raises its internal temperature as a natural defense mechanism to kill or slow down the virus. Most viral fevers are self-limiting, meaning they go away within a few days with proper rest and hydration. However, ignoring it can sometimes lead to complications, especially if it is a symptom of a more serious viral disease such as dengue, influenza, or hepatitis.
Understanding viral fever is the first step toward recovery. By knowing what it is, you’ll be able to take timely action and follow effective measures to recover quickly.
Common Causes of Viral Fever
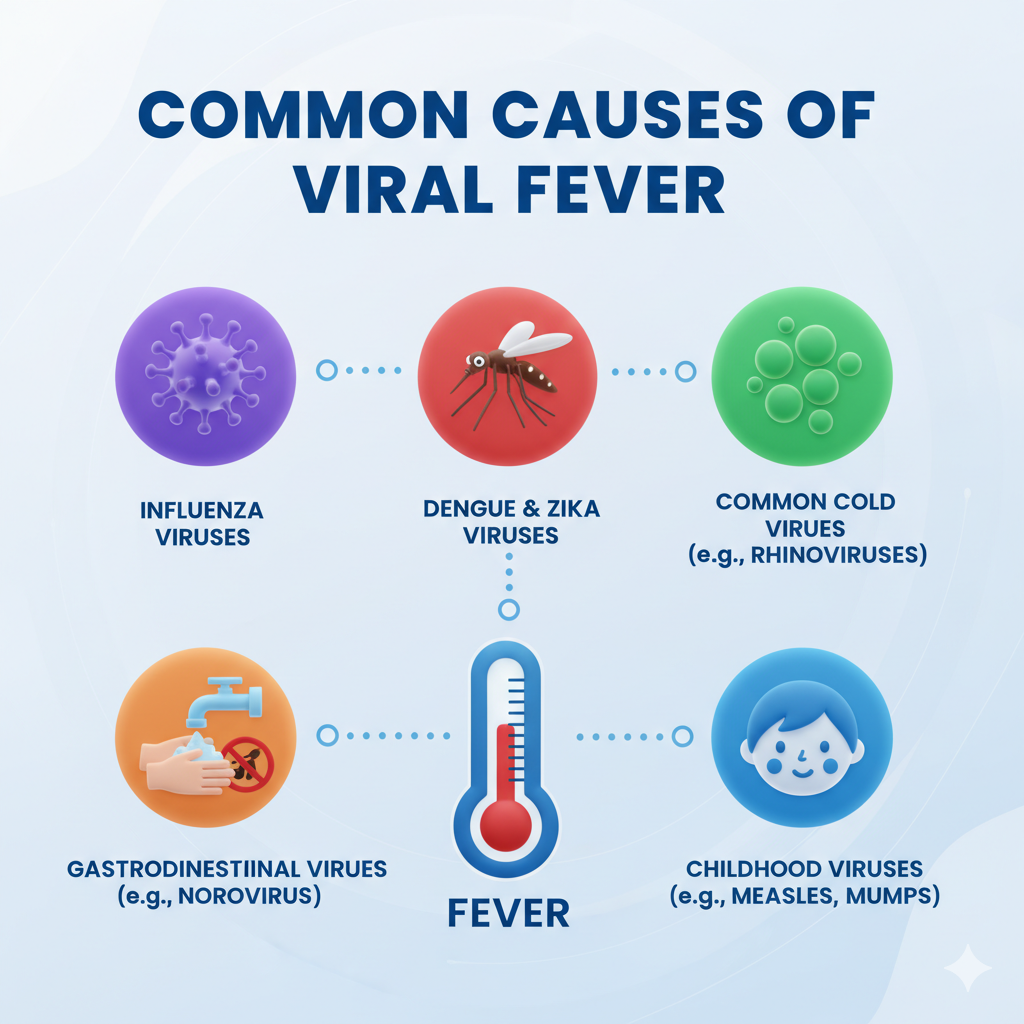
Viral fever can be triggered by several factors, and most of them are related to viral infections spreading through direct or indirect contact. Some common causes include:
- Airborne viruses – Viruses like influenza spread through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Contaminated food and water – Consuming contaminated food or water can cause viral gastroenteritis or hepatitis.
- Mosquito bites – Dengue, chikungunya, and Zika virus are transmitted through infected mosquito bites.
- Seasonal changes – Sudden weather changes, especially during monsoon and winter, make people more prone to viral infections.
- Weakened immunity – People with low immunity, such as children and the elderly, are more vulnerable to viral fevers.
Recognizing these causes helps you not only treat viral fever but also prevent it in the future. For example, maintaining hygiene, avoiding street food during monsoons, and protecting against mosquito bites can reduce your risk significantly.
Typical Symptoms of Viral Fever

The symptoms of viral fever can vary depending on the type of virus causing the infection. However, some common signs include:
- Persistent fever (100°F to 104°F)
- Chills and body shivering
- Muscle pain and body aches
- Fatigue and weakness
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Sore throat and cough
- Runny nose or nasal congestion
- Diarrhea and vomiting in some cases
One important point to remember is that viral fever symptoms often resemble those of other illnesses like malaria or bacterial infections. That is why diagnosis through proper tests is crucial. If your fever lasts more than 3–5 days, you must have a free doctor consultation to rule out serious conditions.
Importance of Early Diagnosis in Viral Fever

Why Early Diagnosis Matters
When it comes to viral fever, early diagnosis can make a huge difference in recovery speed. Most people try to self-medicate with over-the-counter drugs, which may suppress symptoms but delay proper treatment. Early detection helps identify whether the fever is a simple viral infection or a symptom of something more severe, like dengue or typhoid.
For instance, dengue fever can start with mild viral symptoms but quickly worsen if not diagnosed on time. Similarly, typhoid fever presents with prolonged fever, which can be mistaken for viral fever if tests are not done. Early diagnosis ensures that you receive the right treatment, avoid complications, and recover much faster.
Mandatory Tests for Viral Fever
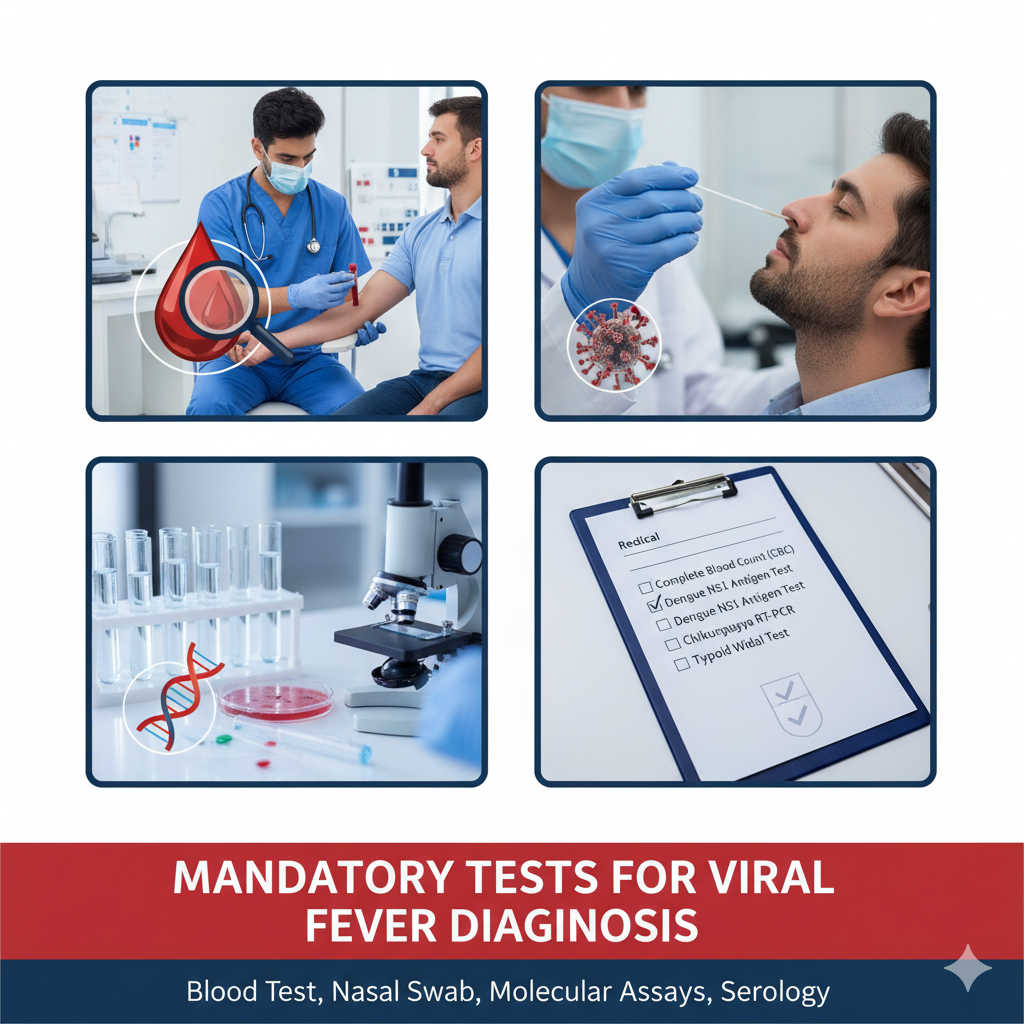
To confirm whether your fever is viral or something else, doctors usually recommend certain tests. These tests not only help in diagnosis but also in preventing complications. Some of the mandatory tests in viral fever include:
Blood Test
A general blood test helps in detecting infections and ruling out bacterial causes.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This CBC test measures different components of the blood. Low platelet counts can indicate dengue, while elevated white blood cells may suggest bacterial infections.
Dengue, Malaria, and Typhoid Tests
Since these illnesses often mimic viral fever, tests such as Dengue NS1 antigen, malaria parasite test, and Widal test (for typhoid) are mandatory if the fever persists beyond 3 days.
Liver and Kidney Function Tests
These tests are recommended if fever is prolonged, as some viral infections affect vital organs like the liver (hepatitis) and kidneys.
By undergoing these tests, you get a clear picture of what is causing the fever. This way, you can take the right steps and recover faster without unnecessary delays.
Home Remedies for Viral Fever Recovery

Importance of Rest
One of the most effective and natural ways to recover from viral fever fast is to get plenty of rest. When you are down with a fever, your body is already working hard to fight off the virus. Engaging in physical or mental stress can slow down the healing process.
Rest helps in:
- Conserving energy for immune function
- Reducing fatigue and body aches
- Lowering stress on the heart and lungs
- Speeding up tissue repair
Even if the fever feels mild, avoid strenuous activities, late nights, or overexertion. Bed rest for at least 2–3 days can make a noticeable difference in your recovery time.
Hydration and Fluid Intake
Staying hydrated is another key factor in recovering quickly from viral fever. Fever causes sweating, which leads to loss of fluids and electrolytes. Dehydration can worsen fatigue, headaches, and muscle cramps.
Some of the best fluids to consume during viral fever include:
- Warm water
- Fresh fruit juices
- Coconut water
- Clear soups and broths
- Herbal teas
Avoid caffeinated drinks and alcohol as they can dehydrate you further. Consistent hydration keeps your body temperature stable and supports faster recovery.
Light and Nutritious Diet
Your appetite may drop during viral fever, but eating the right foods is crucial for healing. A light, easily digestible, and nutritious diet helps supply energy and boosts immunity.
Good food choices during viral fever include:
- Rice porridge and khichdi
- Fresh fruits like bananas, apples, and papayas
- Steamed vegetables
- Boiled eggs and soups
- Yogurt and probiotics for gut health
Avoid oily, spicy, and processed foods, as they may irritate your stomach and slow recovery. Eating small, frequent meals works better than forcing heavy meals.
Herbal Remedies for Viral Fever
Certain natural remedies can provide relief and speed up recovery. Herbal remedies have been used for centuries to reduce fever and boost immunity. Some effective ones include:
- Tulsi (Holy Basil) tea – Helps reduce fever and fight infections
- Ginger tea – Has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties
- Honey with warm water – Soothes sore throat and boosts energy
- Turmeric milk – Acts as an immune booster and aids recovery
These remedies are not substitutes for medical treatment but work well alongside prescribed care to help you recover from viral fever faster.
Medical Treatments for Viral Fever

Role of Antipyretics
When suffering from viral fever, one of the most uncomfortable symptoms is the high temperature itself. This is where antipyretics—commonly known as fever-reducing medications—play a vital role. These medicines, such as paracetamol, are designed to bring down body temperature, relieve headaches, and reduce muscle pain. While they do not kill the virus, they make the recovery process easier by alleviating the discomfort that comes with fever.
Taking antipyretics at the right dosage is very important. Overusing them can strain the liver, while underdosing may not provide enough relief. Doctors usually recommend taking them only when the fever goes above 100.4°F (38°C) or when body aches become unbearable. It is also important not to mix multiple fever medicines without medical advice.
In addition to oral medications, some patients may benefit from cooling techniques like sponge baths with lukewarm water. However, cold showers should be avoided, as they can cause chills and worsen discomfort. By balancing medication with natural cooling methods, you can recover faster and more comfortably.
When Antibiotics are Needed
A common mistake many people make is taking antibiotics for viral fever. Antibiotics work against bacteria, not viruses. This means that in most cases of viral fever, antibiotics are unnecessary and ineffective. Overusing antibiotics without reason can also lead to antibiotic resistance, which makes bacterial infections harder to treat in the future.
However, in some cases, viral fever may weaken the immune system and lead to secondary bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, throat infections, or urinary tract infections. In these situations, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the bacterial complication, not the viral fever itself.
The golden rule is simple: never self-prescribe antibiotics. Only a medical professional can determine whether they are needed. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily may give a temporary sense of relief, but it does not speed up viral fever recovery. Instead, focus on hydration, rest, and supportive care while following your doctor’s advice.
Importance of Medical Supervision
While many viral fevers resolve on their own within a week, medical supervision is essential if symptoms persist or worsen. Prolonged fever, persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, or severe body weakness may indicate a more serious condition.
Doctors not only help in prescribing the right medicines but also guide you on which tests are required to rule out dangerous infections. For example, dengue and malaria often begin with symptoms that resemble viral fever. Without medical advice, such conditions can go unnoticed until complications arise.
Regular monitoring of vital signs like body temperature, blood pressure, and oxygen levels is also important in severe cases. Medical supervision ensures that treatment is tailored to your needs and prevents unnecessary risks. If you are unsure whether your fever is viral or bacterial, consulting a doctor is always the safest choice.
Lifestyle Changes to Speed Up Recovery

Importance of Sleep
Sleep is one of the most powerful tools for healing, yet many people underestimate its role in recovery. When your body is battling a virus, sleep helps restore energy, strengthen immunity, and repair damaged tissues. During deep sleep, your immune system produces cytokines, which are proteins that fight infection and inflammation.
Lack of sleep not only delays recovery but can also make you more vulnerable to recurring infections. Adults should aim for at least 8 to 9 hours of sleep during viral fever recovery, while children may need even more.
To improve sleep quality, try keeping your bedroom cool and quiet, avoiding screens before bedtime, and practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing. A consistent sleep schedule allows your body to focus entirely on fighting the infection, making recovery much faster.
Stress Management During Illness
Stress is often overlooked during illness, but it has a direct impact on how fast you recover. High stress levels release hormones like cortisol, which weaken your immune system and make it harder to fight off viral infections.
Managing stress during viral fever can be as simple as practicing relaxation techniques. Meditation, light breathing exercises, or listening to calming music can reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being. Reading a light book or journaling your thoughts can also help distract your mind from discomfort.
Remember, viral fever recovery is not just about the body—it’s about the mind too. Keeping a positive outlook and reducing stress creates the right environment for healing. Think of it as giving your immune system a helping hand in the battle against the virus.
Hygiene and Sanitation Practices
Viral infections often spread through contaminated surfaces, air droplets, or direct contact. Practicing proper hygiene during recovery is essential not only for your own health but also to protect others around you.
Some essential hygiene practices include:
- Washing hands regularly with soap and water
- Using hand sanitizers when outside
- Wearing a mask if you have cough or cold symptoms
- Avoiding sharing utensils, towels, or bedding with others
- Disinfecting frequently touched surfaces like doorknobs, phones, and switches
Maintaining hygiene reduces the risk of reinfection and prevents the spread of the virus within families and communities. Simple sanitation habits go a long way in ensuring a safe and fast recovery from viral fever.
Boosting Immunity for Faster Recovery

Foods that Strengthen Immunity
Your immune system is your body’s natural defense against viruses, so strengthening it can help you recover faster. The right foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that boost your immunity and speed up healing.
Some of the best immune-boosting foods include:
- Vitamin C-rich fruits like oranges, lemons, and guavas
- Leafy greens such as spinach and kale
- Protein-rich foods like lentils, beans, and eggs
- Probiotics such as yogurt and kefir for gut health
- Nuts and seeds for healthy fats and zinc
Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and fried items, as they can weaken your immune system. Instead, focus on fresh, home-cooked meals that are light and nutrient-dense. Eating immunity-boosting foods ensures that your body can fight the virus more effectively.
Natural Supplements for Recovery
In addition to food, natural supplements can also support recovery from viral fever. Supplements like vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc are well-known for their immune-boosting properties. Herbal supplements such as echinacea, elderberry, and ashwagandha may also help strengthen resistance to viral infections.
However, supplements should never replace a healthy diet. They work best as supportive aids when combined with proper nutrition and rest. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements, especially if you are already on prescribed medication.
Boosting Immunity for Faster Recovery
Hydration as a Key to Immunity
Hydration isn’t just about quenching thirst—it’s a vital part of your body’s healing process. When you have viral fever, your body loses fluids through sweating, vomiting, and sometimes diarrhea. This fluid loss can lead to dehydration, which in turn weakens immunity and slows recovery.
Water helps carry nutrients and oxygen to your cells, flush out toxins, and regulate body temperature. Dehydration, on the other hand, causes fatigue, dizziness, and makes the fever feel worse.
To boost immunity through hydration, try the following:
- Drink 2–3 liters of water daily, depending on your body needs.
- Add oral rehydration solutions (ORS) or electrolyte-rich drinks if you’re sweating excessively.
- Sip on herbal teas like ginger, tulsi, or chamomile for additional antiviral benefits.
- Include water-rich foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges.
Proper hydration gives your immune system the support it needs to fight the infection more effectively, helping you bounce back faster.
Role of Exercise After Recovery
While rest is critical during viral fever, light exercise plays a role in strengthening immunity once you start feeling better. Physical activity improves blood circulation, enhances lung capacity, and boosts the production of immune cells that protect against infections.
However, returning to exercise too quickly can strain your body. The right approach is gradual:
- Start with gentle stretches and breathing exercises.
- Progress to short walks or yoga sessions as your energy returns.
- Avoid high-intensity workouts for at least two weeks after recovery.
Think of your body like a battery that needs recharging. Overexerting too soon can drain your energy, but steady and moderate activity can recharge your immune defenses, making you stronger against future viral infections.
Preventing Viral Fever in the Future

Seasonal Precautions
Viral fevers often spike during certain seasons, especially the rainy and winter months. Sudden changes in temperature, increased mosquito breeding, and contaminated water all contribute to higher infection rates.
To protect yourself during these times:
- Wear weather-appropriate clothing to avoid sudden chills.
- Use mosquito repellents and sleep under nets in high-risk areas.
- Drink only boiled or filtered water.
- Avoid street food and unhygienic eateries during monsoons.
- Strengthen immunity with seasonal fruits like guavas, oranges, and papayas.
By taking these precautions, you reduce the chances of falling sick when viral infections are most common.
Vaccination and Viral Fever Prevention
Vaccinations play an important role in protecting against specific viral diseases such as influenza, hepatitis, and measles. While not all viral fevers can be prevented through vaccines, staying up to date with immunizations reduces the severity and frequency of infections.
For example:
- Flu shots help reduce seasonal influenza.
- Hepatitis vaccines protect the liver from viral infections.
- Childhood vaccinations prevent diseases like measles, mumps, and rubella.
Consult your doctor about which vaccines are necessary for you or your family members. Vaccination is a long-term investment in immunity that reduces the risk of recurrent viral fevers.
Building Daily Healthy Habits
Preventing viral fever isn’t about one big change—it’s about adopting small, consistent habits that strengthen immunity and reduce exposure to infections.
Some powerful daily habits include:
- Washing hands before meals and after returning home.
- Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Sleeping at least 7–9 hours every night.
- Exercising regularly to keep the body active.
- Managing stress with meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
- Staying hydrated throughout the day.
These lifestyle changes not only help in preventing viral fever but also improve overall health and well-being. When your body is strong, it becomes more resilient against infections.
When to Seek Emergency Help

Warning Signs of Complications
Most viral fevers are mild, but some cases can develop into life-threatening conditions if ignored. Knowing the warning signs is crucial to prevent complications.
Seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
- High fever above 104°F (40°C)
- Severe dehydration (dry mouth, dizziness, very low urine output)
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
- Breathing difficulties or chest pain
- Severe headache, stiff neck, or sensitivity to light
- Continuous low platelet count (possible sign of dengue)
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (possible hepatitis)
These symptoms indicate that the viral fever might be linked to a more serious underlying condition. Quick medical attention can save lives in such situations.
Why Ignoring Symptoms Can Be Risky
Some people try to “push through” viral fever with self-medication, but this approach is risky. Ignoring symptoms may delay diagnosis and worsen the infection. For example:
- A prolonged fever could actually be typhoid or malaria.
- Continuous weakness may signal hepatitis or mononucleosis.
- Ignoring dehydration can lead to kidney issues.
Instead of hoping the fever will go away, it’s safer to seek professional medical advice if symptoms persist beyond 3–5 days. Early medical help not only prevents complications but also shortens recovery time.
Conclusion
Recovering from viral fever fast requires a balanced approach—early diagnosis, proper medical care, rest, hydration, a nutritious diet, and good hygiene practices. While most viral fevers are self-limiting, ignoring them can lead to complications. Simple lifestyle changes like eating healthy, getting enough sleep, and managing stress strengthen your immunity, making your body more resilient to future infections.
The next time you or a loved one faces viral fever, remember these proven tips to ensure a safe and speedy recovery.
FAQs
- How many days does viral fever usually last?
Viral fever typically lasts 3–7 days, depending on the type of virus and overall immunity. Persistent fever beyond this should be checked by a home visit doctor. - Which tests are mandatory during viral fever?
Mandatory tests include a complete blood count (CBC), dengue and malaria tests, typhoid test (Widal), and sometimes liver function tests and kidney function tests. - Can viral fever be treated at home?
Yes, mild viral fever can be managed at home with rest, hydration, light meals, and fever-reducing medicines. However, medical supervision is needed if symptoms worsen. - Is viral fever contagious?
Yes, many viral fevers are contagious and spread through air droplets, direct contact, or contaminated food and water. Maintaining hygiene helps prevent transmission.
5. What foods should be avoided during viral fever?
Avoid oily, spicy, and processed foods as they are difficult to digest. Instead, focus on light, nutrient-rich meals like soups, porridge, and fresh fruits.


Leave a Reply